Sat-Sun: Non-working days
- Sources of background information
- Pre-processing of aerial and satellite images
- Additional processing to improve image quality
- Organization of the process of obtaining and providing remote sensing data at various stages of field development
- Technology for creating topographic maps 1:10000 - 1:25000
- Application area
The development of oil and gas fields is viewed as the creation of a unified complex of necessary facilities and includes the design, construction, operation, conservation, and decommissioning of oil and gas extraction facilities. Remote sensing data (RSD) play an important role in the design and construction of production wells to ensure the industrial development of fields. Conducting a set of mine surveying and geophysical works involves the use of large-scale topographic maps, which also need to be updated, similar to geological exploration.
The regulations for compiling project technological documents for the development of oil and gas fields provide for the use of RSD when creating targeted geological and field models at all stages of geological exploration and field development, as well as as baseline information for creating digital geological and filtration models. With the use of RSD, schemes for the location of fields on the terrain can be created, indicating major water arteries, settlements, and routes of oil and gas pipeline communications. Engineering and geodetic surveys involve creating the following cartographic materials using RSD:
- Updating topographic and engineering-topographic plans.
- Creating engineering-topographic plans (in graphic, digital, photographic, and other forms), profiles, and other topographic-geodetic materials and data.
- Creating and maintaining enterprise GIS.
- Creating and updating thematic maps, plans, and atlases for special purposes (in graphic, digital, photographic, and other forms).
- Creating a topographic base and obtaining geodetic data for local area monitoring.

In the course of the development, arrangement, and operation of oil and gas fields, continuous construction, reconstruction, and dismantling of field facilities and engineering communications are carried out. In this regard, there is a need to update and compile special plans reflecting the current state of the territory. The initial data for performing this work include decryption standards, archival cartographic materials, as well as archival and current materials from aerial and space surveys.
Sources of Initial Information
The company "GEO INNOTER" provides the acquisition and delivery of aerial and space information as a distributor and processing company from the following information sources:
- Spacecraft with optoelectronic equipment in the ultraviolet, visible, and infrared ranges of the spectrum with ultra-high, high, and medium resolution (0.3–30.0 m), multispectral equipment with medium (5.0–90.0 m) and low resolution (overview) (0.1–1.0 km), as well as hyperspectral equipment.
- Radar satellites equipped with synthetic aperture radars (SAR) with high (0.5–8.0 m), medium (12.5–25.0 m), and low (100–600 m) resolution.
- Aerial carriers (airplanes, helicopters, unmanned aerial vehicles) equipped with digital optical cameras, scanning optoelectronic complexes, hyperspectrometers, IR radiometers, lidars, synthetic aperture radars, and other instruments.
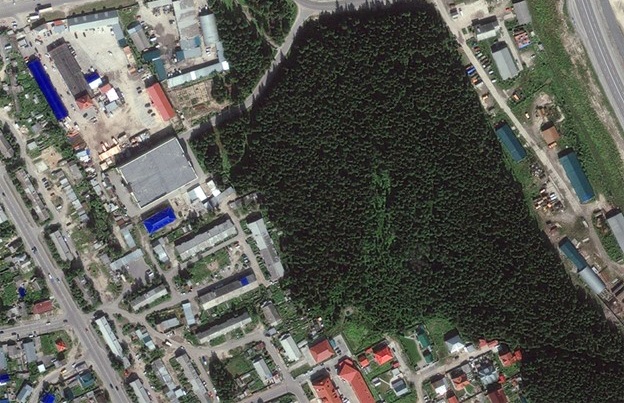

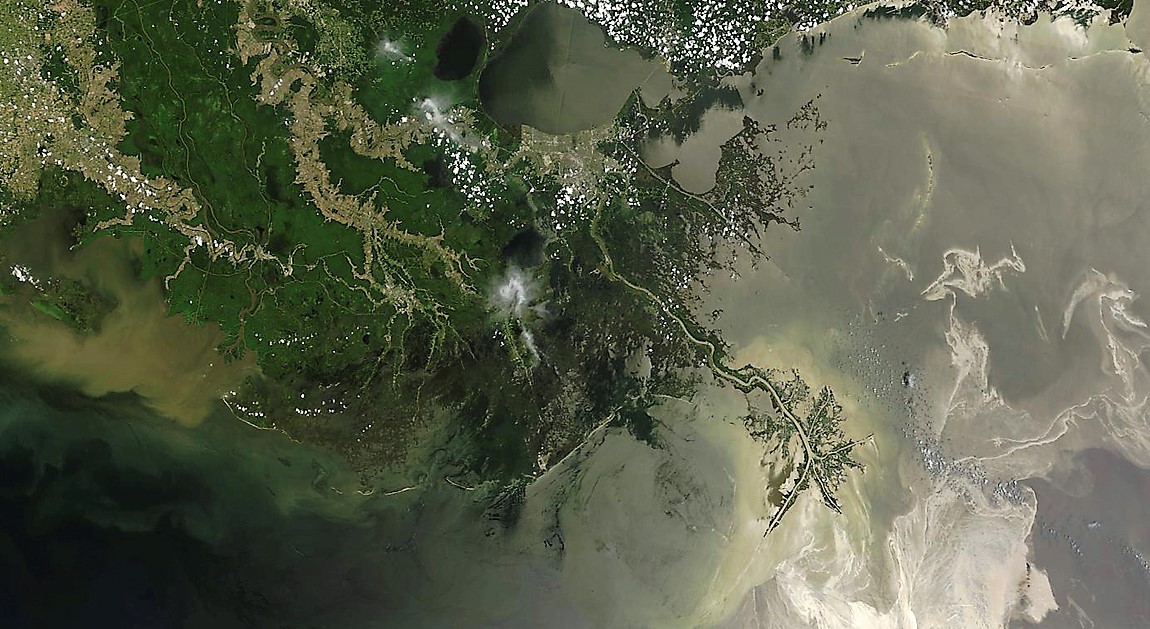
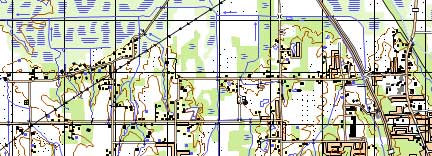
Fig. Fragment of multispectral imaging from the WorldView-2 satellite with a spatial resolution of 50 cm
Preprocessing of Aerial and Space Images
Preprocessing of data transmitted from the spacecraft is typically carried out by the operator. Each remote sensing data operator has its own system and names for processing levels. Generally, the following preprocessing procedures can be distinguished.
For optoelectronic images:
- Radiometric correction – eliminates variations in pixel brightness values resulting from incorrect detector operation, terrain, and atmospheric effects.
- Atmospheric correction – accounts for atmospheric effects, determining the shooting range positions through transparency windows.
- Geometric correction – includes correcting image distortions caused by the sensor (camera), Earth's rotation and curvature, features of the scanner deployment system, striping, line drops, and geocoding – transforming the image into a chosen coordinate system.
For radar images:
- Reception of raw data at the ground personal reception station.
- Formation (synthesis) of a complex-valued radar image.
- Elimination of geometric and radiometric distortions.
- Speckle noise filtering.
The delivery set of space images includes the image itself in raster format (TIFF/GeoTIFF, BMP, IMG, PIX, PCX, etc.) and metadata describing the image formation process, the spacecraft's position at the time of shooting, and the correction level parameters the image has undergone. Metadata may also contain some parametric values describing the relationship between the coordinates on the image and their corresponding coordinates on Earth, such as RPC coefficients, which enhance the accuracy of geometric correction of images and reduce the number of control points.
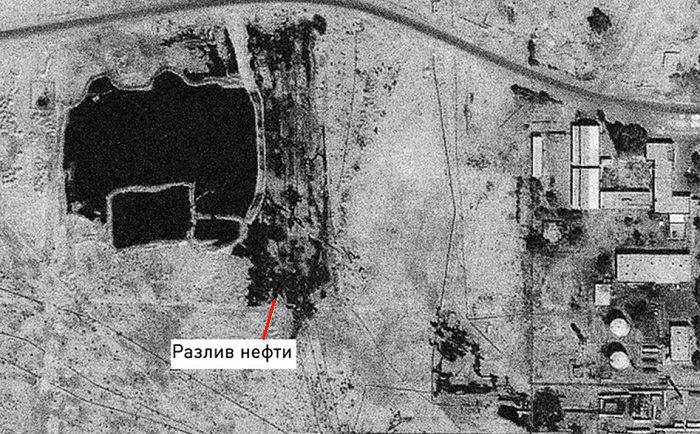

Fig. Fragment of radar imaging
Additional Processing to Enhance Image Quality
"GEO INNOTER" performs additional image processing to improve image quality and obtain color or synthesized images, including:
- Contrasting the image to enhance contrast by equalizing and normalizing image contrast.
- Filtering – a transformation that enhances object reproduction, suppresses unwanted veiling glare and other random noise, emphasizes structural lines, and smoothens the image.
- Fourier transformation improves image quality by decomposing it into multiple spatial-frequency components.
- Color transformation by combining multiple spectral image channels to obtain natural or false color.
- Image fusion (pan-sharpening) – merging panchromatic images with high spatial resolution and color information with low spatial resolution to obtain high-resolution multispectral images.
Organization of Remote Sensing Data Acquisition and Provision at Various Stages of Field Development:
- Receipt and coordination of data from the Client. Agreement on the purpose of obtaining and providing remote sensing data, the size and nature of the area, requirements for processing level, accuracy, and type of images for cost and timeline estimation.
- Planning and ordering of imaging. Depending on the size of the area and other object information, the choice and order of imaging type, as well as other source data, are made.
- Additional processing of materials. Specialized software products available at GEO "Innoter" allow improving the quality of original images and obtaining color or synthesized images with the required accuracy and quality for the Client.
- Transfer of materials to the Client. The results of the work are transferred to the Client in the required format and form.
The development of oil and gas fields involves the creation of a complex of facilities for hydrocarbon extraction, transportation, preparation, and processing, including stages of design, construction, operation, conservation, and decommissioning of oil and gas complex objects.
The regulation for the preparation of project documents for the development of oil and gas fields, as well as the execution of engineering and geodetic surveys at all stages of field development, provides for the creation and updating of topographic and engineering-topographic maps, including topographic maps (plans) with existing and planned development objects at scales of 1:10000 – 1:25000.
TECHNOLOGY FOR CREATING TOPOGRAPHIC MAPS (PLANS) WITH EXISTING AND PROJECTED FACILITIES AT A SCALE OF 1:10000 – 1:25000.
Creating topographic maps (plans) with existing and projected facilities is based on existing topographic and geodetic survey materials and facility design materials using new satellite imagery with a resolution of at least 1.0 meter for a scale of 1:25,000 and at least 0.5 meters for a scale of 1:10,000. Photogrammetric and cartographic work includes:
- Collection, systematization, analysis of initial materials, and development of a work program.
- Creation of plan-height justification for satellite imagery.
- External orientation and orthotransformation of satellite images.
- Deciphering existing field development facilities and plotting projected facilities.
- Digitization of necessary content elements and obtaining vector layers of the created map (plan).
- Accuracy and quality control of the created maps (plans), formation of the final product, and delivery set as specified by the Customer's Technical Assignment.

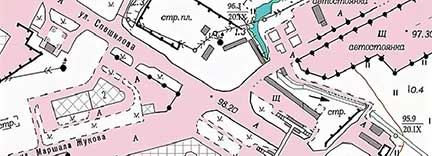
Fig. Fragment of a topographic plan at a scale of 1:10,000
APPLICATION AREA
Obtaining and providing remote sensing data (RS) at various stages of field development is intended for design, survey, and construction organizations in the oil and gas sector and other interested organizations for the purpose of:
- Conducting engineering and geodetic surveys for new construction sites.
- Ensuring the safe operation of enterprises, buildings, structures, pipeline transport, and field operations.
- Carrying out reconstruction, major repairs, and restoration of facilities, including buildings, structures, and oil and gas transportation system facilities.
To order work for obtaining and providing remote sensing data at various stages of field development, contact us by phone at +7 495 245-04-24, or send a request to e-mail: innoter@innoter.com