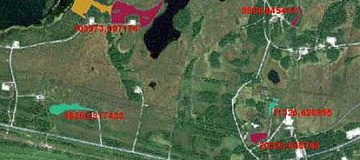
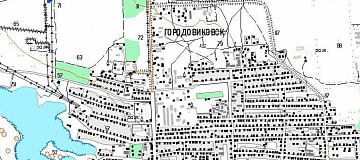
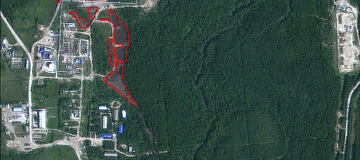
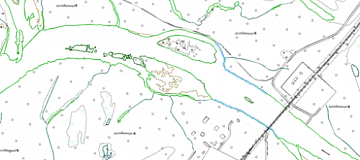
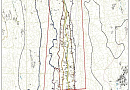
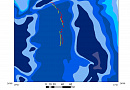
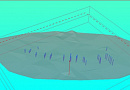
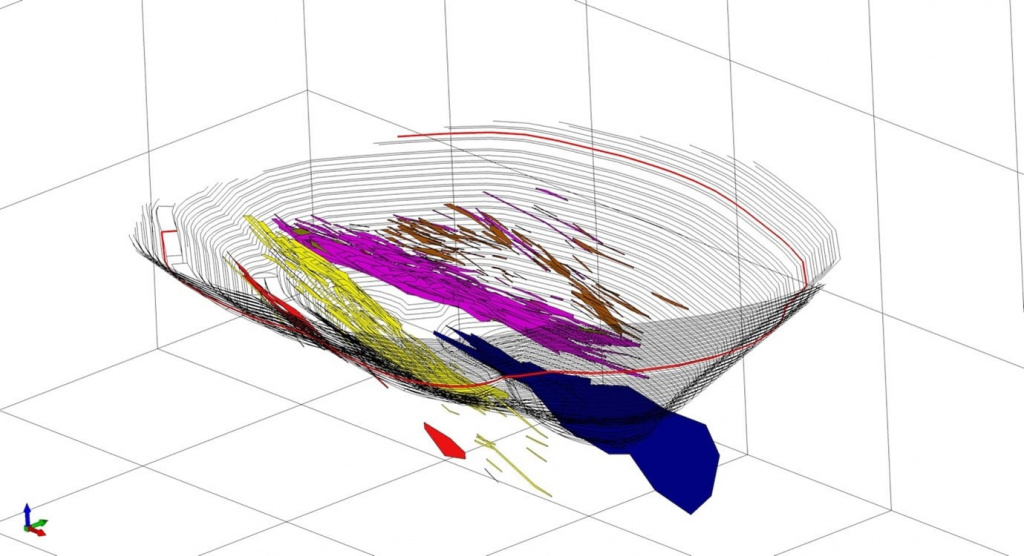
Geological modeling or geomodeling is the creation of representations or numerical equivalents of parts of the Earth's crust, both on and beneath its surface.
Geological modeling (geomodelling) is an applied science that involves creating computerized representations of parts of the Earth's crust based on geophysical and geological observations.
Geological modeling (geomodeling) is associated with the concept of a comprehensive Earth model (an interdisciplinary, interoperable, and updatable knowledge base about the Earth's subsurface). Geological modeling (geomodeling) is used for managing natural resources, identifying natural hazards, and quantitatively assessing geological processes, primarily applied to oil and gas fields, groundwater aquifers, and mineral deposits.

You can order from us
Prices for services
| Consultation | Free |
|---|---|
| Preliminary analysis of materials, preparation of technical task | Free |
| Work of technical specialists and experts | From 100,000 rubles |
| TOTAL COST | From 100,000 rubles |
Cost depends on:
- area of the site of interest (work area);
- complexity of the terrain;
- seasonality of work;
- advance payment amount;
- required computational power;
- geological complexity of the site;
- and others.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
The completion time of the work is from 20 business days from the date of receiving the advance payment and is calculated individually for each customer.
The completion time of the work depends on:
- the total area of the territory of interest;
- requirements for the final product.
The service delivery time depends on the complexity of the work and is calculated individually for each customer.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
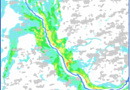
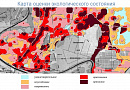
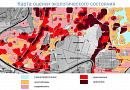
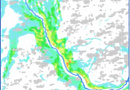
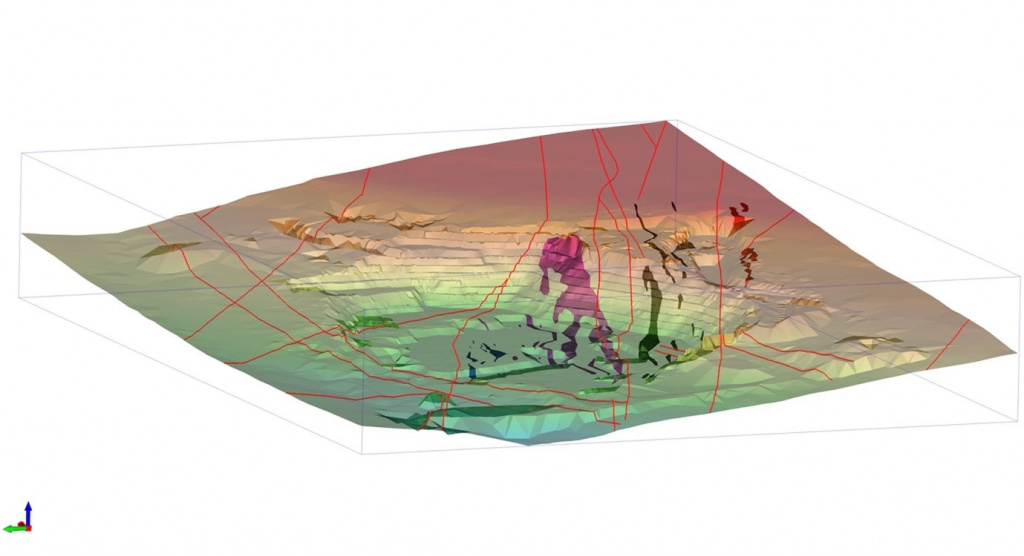
The Customer receives a geological map with a structural three-dimensional model.
Data of various types can be synthesized. The synthesis of available data significantly increases the accuracy and efficiency of modeling.
Requirements for Source Data
Accurate geographical coordinates of the object in the required coordinate system (specialists from GEO INNOTER LLC will clarify the coordinates provided by the Customer in any convenient form).
Sets of optical, IR (near and thermal), and radar images.
All available geological maps of the search area.
Software:
- GIS - QGIS, ArcGIS, etc.
- Processing - ERDAS, ENVI SARscape, SNAP, etc.
- Modeling - Datamine Studio
Related services





Completed projects

Customers




FAQ
Geological modeling (geomodelling) for rapid creation of reliable volumetric models and basic resource estimation includes the following components:
- Wireframing of spatial bodies and surfaces. This involves a set of semi-automatic and interactive 3D tools for creating, modifying, displaying, and evaluating closed and topographic wireframe models.
- Intelligent mineral exploration based on machine learning algorithms and 3D modeling.
- Geostatistical analysis of deposits includes tools for variogram construction, analysis, and interactive fitting of models. It also involves cross-validation of selected variogram models, multiple types of 3D kriging, resource estimation, and more.
- Deposits modeling provides capabilities for constructing, viewing, evaluating, and editing block models of deposits. Metal grade interpolation and other indicators are performed using traditional and geostatistical methods. Visualization, interpretation, and modeling of project data (including Big Data) are also supported.
Licenses
Warranty
We guarantee 100% quality of services. Cooperating with GEO Innoter specialists, you exclude risks and losses!The availability of qualified personnel with extensive experience in working with specialized software allows us to ensure timely and high-quality work!