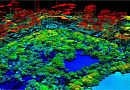
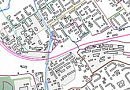
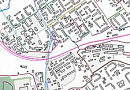
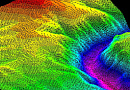
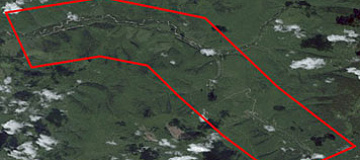
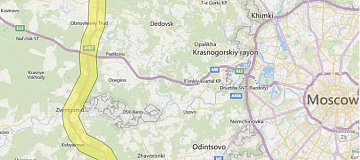
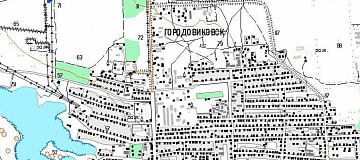
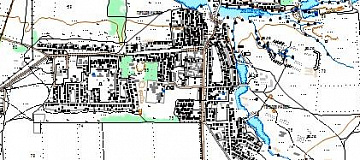
Accessibility Analysis for Transportation Planning is a comprehensive concept defined by the time required to travel from the point of departure to the destination point.
As an important indicator of development, accessibility, and the convenience of the location of a particular area, as well as its investment attractiveness, it needs to be taken into account in various spheres of human activity, including:
- Industrial purposes (developing new territories, planning various construction projects, building infrastructure, etc.);
- Personal purposes (choosing a place of residence, leisure destinations, route planning, travel, etc.).

You can order from us
Prices for services
| Consultation | Free of charge |
|---|---|
| Image acquisition, preliminary analysis | Free of charge |
| Image processing, vectorization, technical report preparation | From $300 USD* |
| Work of technical specialists and expert(s) | From 50,000 rubles |
| Total cost | From 50,000 rubles |
* - free of charge if the Client provides their own materials or if free images can be used.
The cost of analyzing the transport accessibility of a location is calculated individually for each client and depends on: the area of the territory of interest; the cost of suitable satellite images; the level of detail required for identifying and describing the object composition, as well as the accuracy of the georeferencing of the obtained results.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
Term of work - from 10 (ten) working days.The timeframe for the analysis of transport accessibility of the area depends on the total scope of work within the project and terms of reference and is calculated individually for each project.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
- This is a turnkey product, executed according to unified standards, ready for loading into various GIS systems;
- An analytical report (if necessary), representing an analysis of data obtained during the processing of information.
Requirements for Source Data
- Exact location of the area of interest (coordinates, district name, region, SHP file, etc.);
- Desired list of objects for the required analysis of transport accessibility of the area;
- Other relevant information available.
If it is not possible to provide the specified data, please provide information about the purpose for which the remote sensing data materials are planned to be used. The specialists of "GEO INNOTER" LLC will analyze the requirements and propose an optimal solution to the problem.
Related services


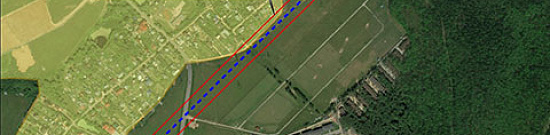

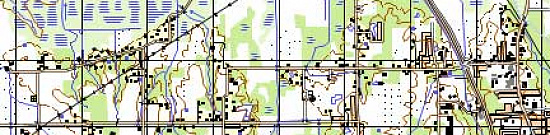




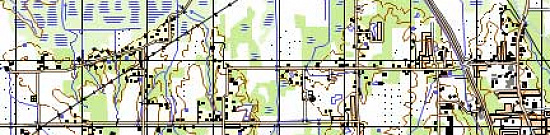

Completed projects

Customers
FAQ
Transport accessibility analysis is an important tool for determining the level of accessibility of a specific location depending on various types of transportation, such as car transport, public transport, pedestrian transport, and so on.
To conduct transport accessibility analysis, the following factors need to be considered:
-
Distance: The distance to the nearest transportation infrastructure, such as bus stops, subway stations, train stations, etc.
-
Travel time: The average time it will take to travel from point A to point B, considering transportation infrastructure and traffic congestion.
-
Transport frequency: The number of transport vehicles passing through a certain point within a specific time frame.
-
Transport infrastructure capacity: The ability of the transport infrastructure to accommodate a certain number of vehicles and people within a specific time frame.
-
Expenses: The cost of transportation services and the ability to afford them.
Transport accessibility analysis can help in making decisions when choosing a location for living, working, or doing business. It can also be used to identify potential issues with transportation infrastructure and find ways to improve accessibility.
In the context of seasonality, analyzing the state of the transportation network is crucial to ensure its efficiency and safety. Seasonality means that the demand for transportation services can significantly vary depending on the time of year, holidays, events, and other factors.
To analyze the state of the transportation network in the context of seasonality, regular surveys and data analysis of traffic flow are necessary to identify potential issues and take measures to address them. Some of the possible measures for analyzing the state of the network in seasonality conditions include:
-
Analysis of traffic flow changes: Observing the number of vehicles on the roads, including cars, trucks, buses, etc., during different seasons and during holidays and events.
-
Monitoring of traffic congestions: Studying information about traffic congestions during different seasons and under different circumstances, such as weather conditions, road accidents, etc.
-
Studying the demand for public transport: Collecting data on the demand for public transport, including the number of passengers and their routes, during different seasons and during holidays and events.
-
Evaluation of the condition of transportation infrastructure: Regular inspection of infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, tunnels, railways, airports, etc., to identify potential problems and risks.
-
Analysis of accident data: Analyzing statistics of road accidents and accidents in other infrastructure areas to identify the most dangerous locations and causes of accidents.
Monitoring the state of the network in seasonality conditions helps identify potential issues and risks and take measures to improve and address them effectively.
Analyzing transportation accessibility is a crucial part of developing new territories. It allows identifying the most efficient transportation methods and planning the construction of new roads and infrastructure, thereby increasing the accessibility of new territories and enhancing their economic potential.
When conducting an analysis of transportation accessibility, several aspects are important to consider:
-
Distance: Evaluate the distance from the new territories to the nearest settlements, important facilities, and centers of economic activity.
-
Types of transportation: Study the accessibility of various types of transportation, such as automotive, railway, air, water, and others.
-
Road infrastructure condition: Assess the condition of road infrastructure and identify potential issues with establishing new roads.
-
Transportation load: Examine the level of traffic load on existing roads and routes to determine the need for new roads and highways.
-
Transportation cost: Evaluate the cost of transporting goods and passengers and identify the most economically advantageous transportation methods.
-
Environmental factors: Consider environmental factors, such as emissions of harmful substances and pollution, that may arise during the construction of new roads and the development of transportation infrastructure.
Analyzing transportation accessibility enables the identification of the most effective ways to develop new territories and formulate plans to improve transportation infrastructure and enhance accessibility for residents and businesses.
Licenses
Warranty
It is optimal to specify profile RF and international documents regulating the subject area under consideration.We guarantee 100% quality of services. Cooperating with GEO Innoter specialists, you exclude risks and losses!
The availability of qualified personnel with extensive experience in working with specialized software allows us to ensure timely and high-quality implementation of projects!