Sat-Sun: Non-working days
Customer
Ministry of Natural Resources, Ecology and Environmental Protection of the Republic of Mari ElProject's objective
Monitoring the environmental impact during mining operations and the production of common minerals on the territory of the Republic of Mari El. Identification of illegal subsoil use accompanied by environmental pollution, namely, detection and updating of information about illegal quarries (outside the boundaries of licensed areas) and associated municipal solid waste (MSW) dumps.Work description
As part of the Customer's technical assignment, cataloging and preliminary photogrammetric processing of archival images were carried out, as well as automatic and manual interpretation, data analysis, and updating of the GIS created in 2013-2016, and fieldwork.
Preparatory work.
Archival imagery for the work areas – satellite images from the Kanopus-V and Resurs-P satellites for 2017-2018 – was ordered. Then, based on metadata, specialists from Innoter LLC cataloged the available remote sensing data, which allowed for the effective selection of suitable images for interpretation and the exclusion of data with a high percentage of cloud cover, snow cover, and other defects.
The next stage of work involved orthorectification (using RPC polygons and SRTM-1) of the selected images, their geometric and radiometric correction, including precise alignment with the images used earlier in the 2013-2016 project.
After this, it was necessary to assess the spectral separability of classes to identify mining objects. The main purpose of spectral separability assessment is to visually or automatically compare spectral brightness curves that determine the reflectivity of various ground cover objects. Test sites were selected in the most characteristic areas for this landscape, as well as mining objects (quarries, forests, anthropogenic objects, non-vegetated land, water bodies).
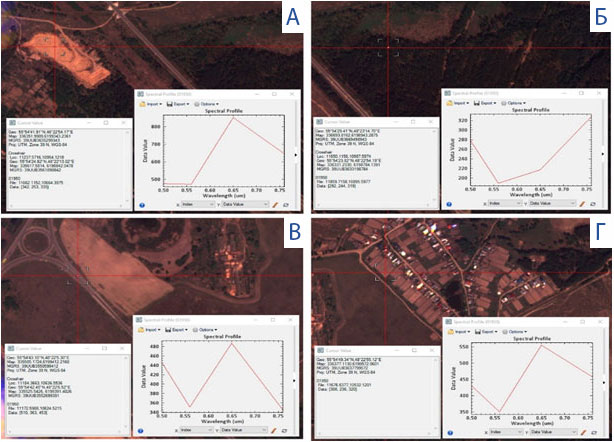
Test sites for assessing the spectral characteristics of landscape objects. (a – sand, b – wood-shrub vegetation, c – asphalt)
Based on this assessment, Innoter LLC specialists were able to determine which objects would be well classified in the images due to different spectral characteristics (e.g., "sand" and "forest"), and which objects are similar in parameters and could be misleading (e.g., "sand" and "soil"), thus requiring more careful selection of reference sites and expert control of automatic interpretation. However, even objects with good references can often be falsely classified in automatic mode, so visual interpretation by specialists is necessary.
Updating and supplementing data of the previously created GIS
In the NextGIS QGIS software product, data was updated using new information obtained from images from 2017-2018, as well as from the quarry registry of the Republic of Mari El, provided by the Ministry of Natural Resources, Ecology, and Environmental Protection of the Republic of Mari El.
The resulting map in GIS format contained geoinformation layers that reflected preliminary information about all objects of the "mining objects" class, quarry areas, information about minerals, presence of dumps, etc.
Example of one of the map layers
Image interpretation and data classification
As mentioned above, the remote sensing data selection was initially carried out. Of the 65 archival images included in the first delivery, only 40 met the time range. Further selection was based on the reliability criteria as a source of information regarding interpretation features. Images with snow cover and continuous cloud cover were excluded. Snow significantly complicates the detection of quarries, for example. Clouds even more so. Thus, priority was given to images taken in the summer-autumn period.

The detected quarry (red polygon) is reliably interpreted in the summer (left) image but not readable in the winter (right) image
As part of the preparation for the main stage of work, a database cluster was launched – a software and hardware complex that allows Innoter LLC employees to work simultaneously on one project using SQL. The advantage of using such a cluster over working in a regular desktop GIS is that many interpretation specialists work simultaneously with the same data: there is no need to duplicate data, consolidate interpretation results from several performers, etc.
In the first stage, the interpretation was done visually by specialists. The following interpretation features were used:
- spectral brightness (photo tone);
- size;
- shape;
- structure;
- shadow;
- context (proximity to roads, settlements);
As a result, preliminary data were obtained.
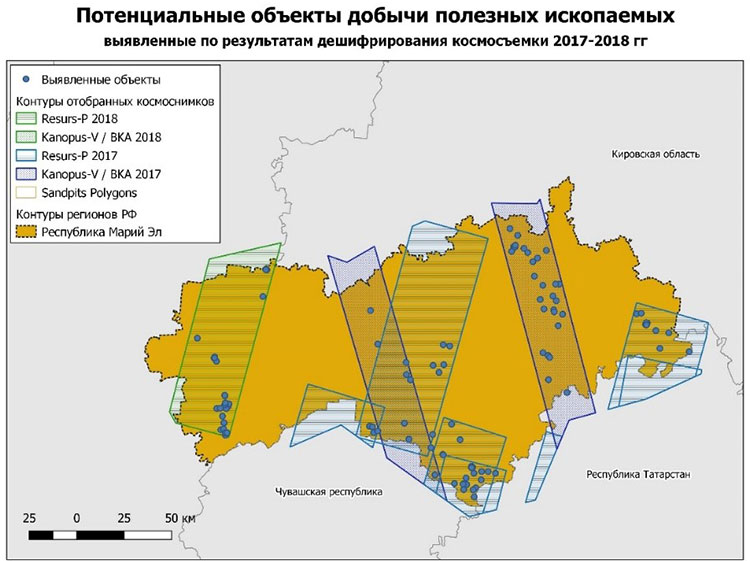
Potential mineral extraction sites identified from the 2017-2018 satellite imagery interpretation results
Further, the digitization of objects of interest was carried out, and then it was decided to perform automatic unsupervised classification of the images (clustering) within the selected quarries. For example, it became possible to identify the worked-out part of the quarries. Several models were created for this purpose, processing the data in a special way (based on the ISODATA method). As a result, several classes were identified, automatically interpreted by the program.
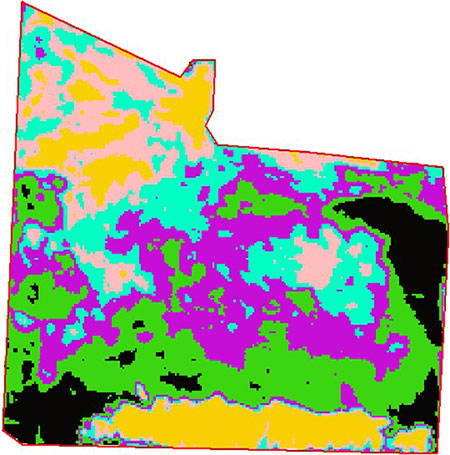
A fragment of the image classified by the quarry boundary. 6 classes are highlighted
In the next stage, the data were also vectorized in automatic mode using a specially created model and combined into one layer.
Analysis of the obtained data
The next significant stage of work was the analysis of the obtained objects in conjunction with the existing data of the mineral resources fund and preparation for field research. In addition to data integration, a special "reliability" scale was developed:
- 25% – the presence of a quarry is unlikely;
- 50% – the presence of a quarry is determined with a moderate degree of probability;
- 75% – the presence of a quarry is determined with a high degree of probability;
- 100% – the object is a quarry.
The data were assessed in accordance with this scale, and all other relevant attribute data were added (quarry condition, presence of a landfill, extraction area, type of mineral, remote sensing image used for interpretation, year of the image).
As part of the preparation for fieldwork, several road graphs were created and routes for surveying the objects of interest were planned.
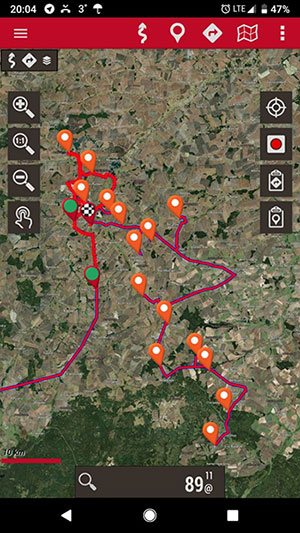
Field route No. 1
Fieldwork
The final stage of the project involved field surveying of the objects of interest. As a result of the fieldwork, 43 potential mining objects were surveyed, and 21 of the 43 visited objects turned out to be quarries.
Moreover, the field survey experience allowed for refining the templates and references for office interpretation, which will help Innoter LLC employees in future similar projects. Now, Innoter LLC has its own bank of interpretation references, and the accuracy of quarry detection reaches 70% or more.
Results
Monitoring of environmental impact during mining operations in the Republic of Mari El was carried out using "Resurs-P" and "Kanopus-V" satellite images from 2017–2018. Taking into account the existing coverage of the Republic's territory with suitable satellite images for interpretation, more than 100 mining objects were identified as a result of the work performed.
The results showed that remote sensing data can – and should – be used for environmental monitoring, for example, in this case, to identify illegal mining and extraction of minerals, as well as to detect unauthorized solid waste landfills.
In addition to the identified mining objects, additional interpretation features of quarries and other objects that can be confused with quarries during automated and manual interpretation were developed.
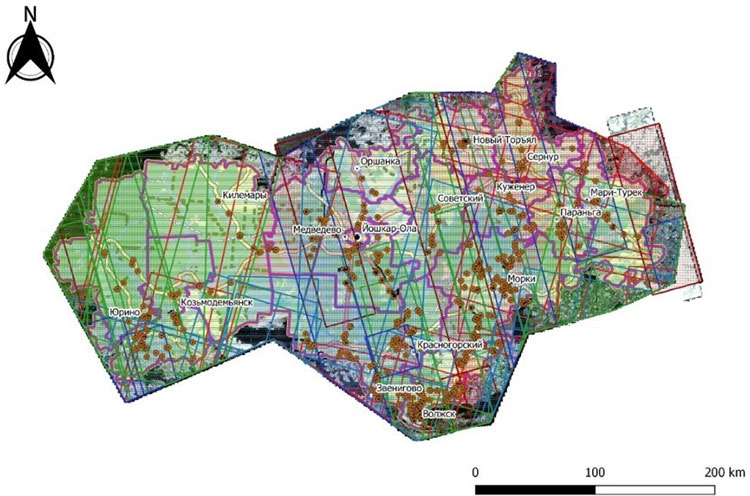
A GIS project for managing and monitoring mining objects in NextGIS QGIS format was compiled, containing information on the outlines of legal and illegal workings ever detected in the Republic; on field survey data and unconfirmed cases of illegal activity (including photo centroids); on the images used in the work. Moreover, the GIS contains topographic and administrative information about the territory.
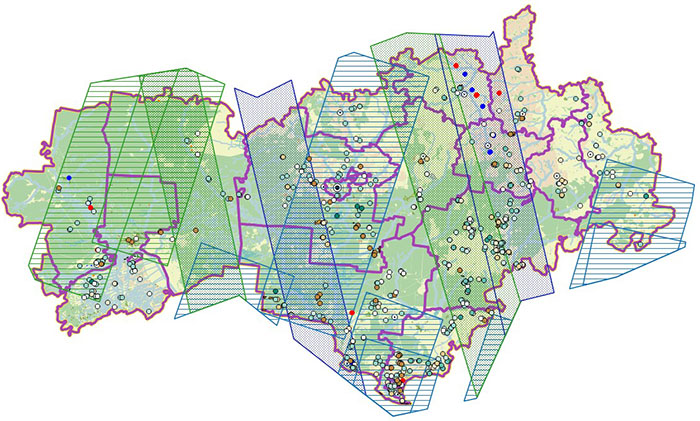
Final view of the created GIS project
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
