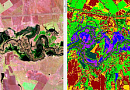
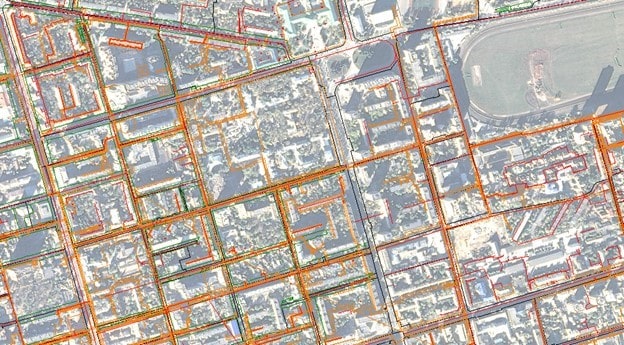
Insurance Risk Assessment is the ability of an insurance company to determine the likelihood of certain losses or damages to the insured object or event, which helps to determine the necessary insurance premium and policy conditions.
Insurance Risk Assessment using Remote Sensing (RS) is a method of risk assessment that utilizes data obtained from satellite Earth observation or through aerial photography or UAVs. This approach allows insurance companies to analyze risks based on detailed geospatial information, such as changes in the natural environment, conditions in a specific region, and other parameters that may affect insurance claims. By using RS, companies can more effectively evaluate and manage insurance risks, contributing to the development of more accurate and tailored insurance products.
You can order from us
Prices for services
| Consultation | free |
|---|---|
| Image Selection, Preliminary Analysis | free |
| Image Order |
From 10 to 600 USD per image (a minimum of two images required) |
| Technical Specialist Work | From 15,000 RUB |
| TOTAL | From 16,000 RUB |
The price depends on the area, complexity, deadlines, and cost of the images and is calculated individually for each customer.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
The completion time for the work is from 7 (seven) working days and is calculated individually for each customer.
The completion time depends on the area, complexity, deadlines, and cost of the images and is calculated individually for each customer.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
GEO INNOTER provides the client with an expert analysis - a written document (geodynamic study containing a technical report) that reflects the process and results of the research conducted using satellite or aerial imagery. The outcome of the study includes conclusions based on the questions posed to the expert and recommendations derived from the analysis.
In summary, the result of the work includes the following documents and materials:
- Expert conclusion signed by the expert and stamped by the organization;
- Technical report (geodynamic study);
- Certificate confirming no changes were made to the RS material (metadata verification and anomaly detection due to machine or manual alterations);
- Copies of the license authorizing the organization to perform such work;
- Copy of the expert's diploma;
- Satellite and UAV images, maps, and other materials if they were purchased separately at the customer's expense and/or provided by the customer to LLC "GEO INNOTER";
- Other documents, charts, etc.
Requirements for Initial Data
- Exact geographic coordinates of the object in the required coordinate system (LLC "GEO INNOTER" specialists will clarify the coordinates provided by the customer in any convenient form).
- Images that meet the research questions based on the criteria of the time of capture, spatial resolution, and availability of the necessary spectral channels, initial georeferencing by RPC.
- Orthorectified images (georeferenced to the terrain) with the required accuracy.
Customers
FAQ
- Analyzing insurance policies and contracts: Checking the terms and conditions of insurance, examining the coverage of insurance coverage.
- Assessing the likelihood of events: Assessing the likelihood of various risks and events that may lead to losses.
- Potential Loss Assessment: Determining possible financial losses resulting from insured events.
- Analyzing historical data and statistics: Studying previous loss events, analyzing trends and patterns.
- Vulnerability assessment: Examining the policyholder's vulnerability to potential risks.
- Assessing the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures: Examination of the policyholder's risk mitigation actions and their impact on potential losses.
- Calculation of financial reserves: Determining the necessary financial reserves to cover losses.
- Forecasting future risks: Assessing the likelihood of new risks and their impact on the insurance.
There are many types of insurance risks, here are some of them:
- Risk of losses from natural disasters: such as earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, fires, and other natural catastrophes.
- Risk of damage from third-party actions: theft, vandalism, as well as liability for causing damage and injuries to third parties.
- Health and life risk: related to loss of health, injuries, illnesses, or death.
- Auto insurance risk: accidents, theft, damage, etc.
- Business interruption risk: potential loss of profit due to reasons leading to the stoppage or reduction of business operations.
- Property risk: damage or loss of property, including homes, cars, equipment, and other valuables.
- Financial risks: associated with investments and financial operations.
- Medical and life insurance: related to medical expenses, life insurance, and disability insurance.
- Technological and cyber risks: potential cybersecurity threats, hacking attacks, data breaches, and other technological risks.
- Political risks: risk of problems arising from political changes, wars, terrorist acts, and more.
Remote sensing of the Earth can help in assessing various insurance risks, including:
- Floods: By analyzing images obtained through remote sensing, areas with a high risk of flooding can be identified and appropriate precautionary measures can be taken.
- Fires: Monitoring territories through remote sensing allows for the detection of early signs of fires and predicting their spread.
- Earthquakes and geological hazards: Remote sensing can be used to monitor tectonically active zones and identify potential earthquake sites.
- Crop losses: Analysis of vegetation data obtained via satellites can help assess crop yields and the risks of crop losses.
- Infrastructure risks: Remote sensing can be applied to monitor the condition of infrastructure, identify defects, and assess the risk of collapses.
- Environmental risks: Utilizing remote sensing data allows for monitoring the state of the environment, controlling water and air pollution, and identifying and preventing environmental disasters.
Using remote sensing for assessing insurance risks offers several advantages:
- Broad coverage and regular data updates: Satellites used for remote sensing can cover extensive areas, allowing for data collection over large areas in a short time. This enables timely detection of changes and risks.
- Objective assessment: Remote sensing data is objective and not subject to subjective influences. This contributes to a neutral and accurate risk assessment.
- Multidisciplinary approach: Remote sensing allows the use of data from various spectral ranges to analyze different aspects of risks, including geographical, climatic, ecological, and others.
- Cost-effectiveness: Compared to traditional monitoring and risk assessment methods, remote sensing can be more cost-effective in terms of data collection and analysis.
- Predictive capabilities: Remote sensing data can be used for predicting potential risks and events, which helps in taking preventive or mitigative measures.
Licenses
Warranty
We guarantee 100% quality of services. Cooperating with GEO Innoter specialists, you exclude risks and losses!The availability of qualified personnel with extensive experience in working with specialized software allows us to ensure timely and high-quality work!