You can order from us
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Customers
FAQ
Land administration is the process of planning, development, utilization and protection of land and natural resources related to land use. It includes coordination and management of various aspects of land use, such as agrarian management, forestry, urban planning, development, nature conservation and environmental sustainability.
Land administration aims at the efficient use of land in accordance with the goals and needs of society, while taking into account environmental, economic and social aspects. It includes the development of land use policies, legislative norms and regulations, as well as mechanisms for controlling and monitoring land use.
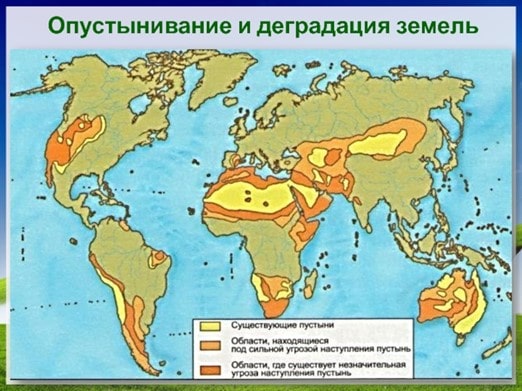
The objectives of land management include ensuring food security, preserving biological diversity, preventing negative human impact on natural ecosystems, promoting sustainable development, improving the living conditions of the population and equitable distribution of land rights.
The main tasks of land resources management include planning of land use, administrative regulation of land relations, allocation and distribution of land plots, control over land use, protection of soil and water resources, regulation of land conflicts and dispute resolution.
The main tasks of land resources management include planning of land use, administrative regulation of land relations, allocation and distribution of land plots, control over land use, protection of soil and water resources, regulation of land conflicts and dispute resolution.
Land resources management is carried out by state bodies, local authorities, land experts, public organizations and stakeholders, taking into account the principles of sustainable development and public participation.
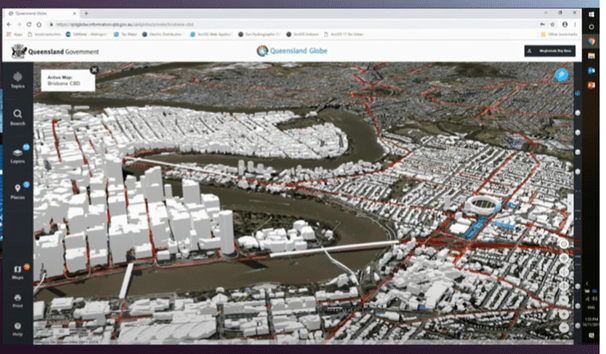
Remote sensing land management is the application of modern technology to monitor, analyze and manage land resources. It is an area where resources, rights, sites and governments interact with remotely sensed land technologies for effective land use management.
State and municipal authorities play an important role in land management by utilizing data obtained from remote sensing of land. They can use this information to make decisions on the location of facilities, planning the use of land parcels, controlling compliance with land use rules and regulations, protecting natural resources and protecting the environmental sphere.
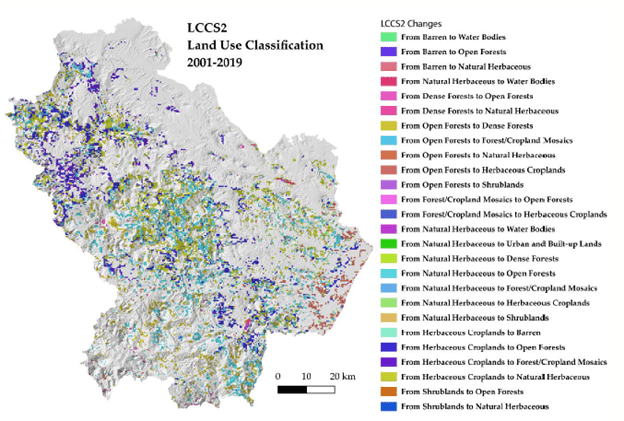
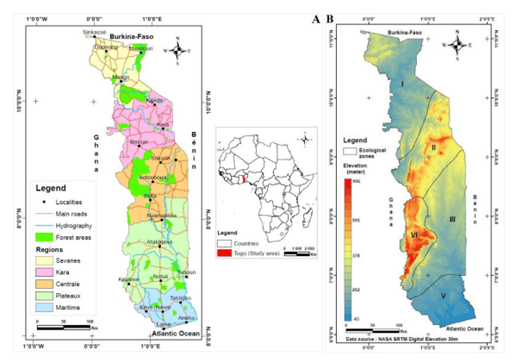
Remote sensing of land provides a variety of data about the land, such as information on vegetation, land cover, water levels, and other environmental parameters. These data can be used to determine optimal land use, plan agricultural operations, monitor forest resources, assess ecological status, and monitor changes in the landscape.
Remote sensing of land can also help in establishing legal relations in the sphere of land use. It can be used to determine the boundaries of land plots, establish ownership rights, control land use in accordance with legislation and resolve land disputes.
Russian experience shows that remote sensing of land can be an effective tool in land management. It allows obtaining up-to-date and objective data, reduces monitoring costs and ensures more effective planning and control over land use.
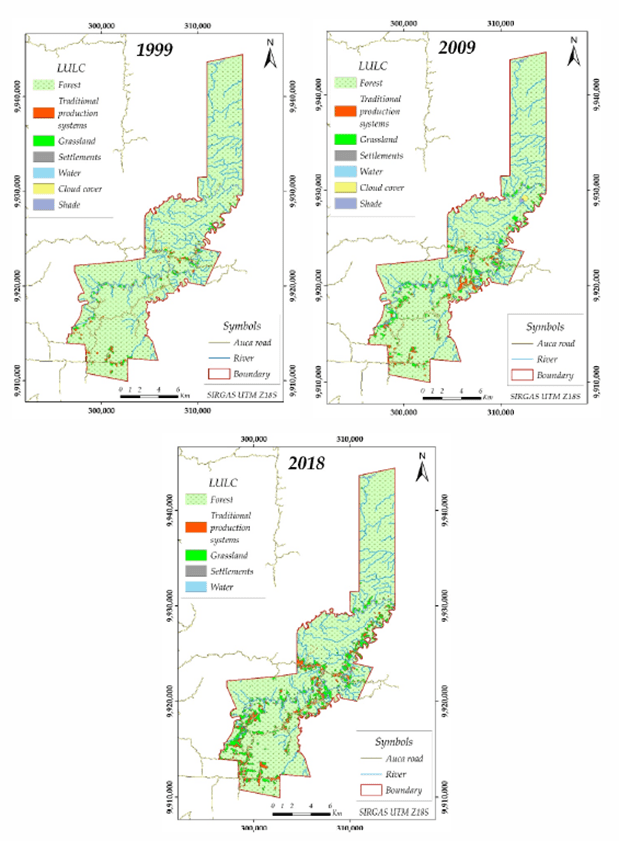
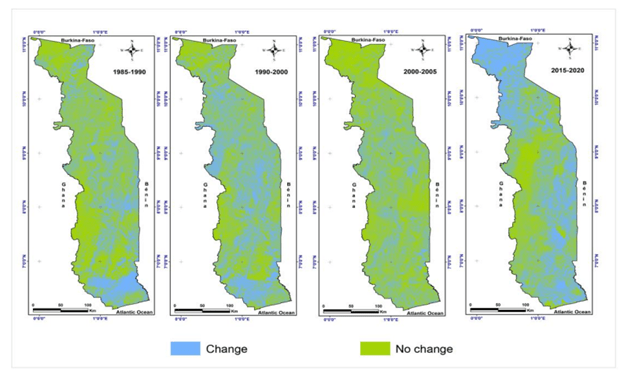
Various types of activities are carried out as part of land management using remote sensing. One of them is monitoring changes in land use. Remote sensing of land can be used to track changes in land cover over time, identifying new development, changes in agriculture or forest cover. This allows the effectiveness of current land use strategies to be assessed and evidence-based decisions to be made.
Another aspect of land management using remote sensing of land is related to planning the use of land parcels. The analysis of remotely sensed data makes it possible to identify suitable land parcels for various purposes such as agriculture, industry, residential areas or protected areas. This helps to optimize the use of land resources, taking into account the requirements and needs of different sectors of the economy and society.
Also, remote sensing of land can be used to monitor compliance with land use rules and regulations. The data obtained from remote sensing can detect illegal changes in land use or violations of environmental norms. This contributes to effective control over the use of land resources, observance of rights and prevention of illegal actions.
State and municipal authorities play an important role in regulating land relations and coordinating land use activities. They monitor and analyze remotely sensed data and make decisions based on the information obtained. In addition, governmental and public organizations can use these data to develop policies and strategies for land management.
Thus, remote sensing of land is a powerful tool in land management. It provides access to a wide range of information on land cover, changes in land use and environmental conditions. This enables informed decisions to be made in the planning, administration and protection of land resources.
Remote sensing of the earth also has a number of advantages. First, it provides the possibility of obtaining data over large areas, including remote and inaccessible areas. This makes it possible to cover vast areas and obtain a comprehensive analysis of land resources.
Secondly, remote sensing of land is a prompt and efficient method of obtaining information. With the help of satellites and other means of observation, periodic measurements and monitoring of the state of the land can be carried out, which allows rapid response to changes and problems.
Third, remotely sensed land data provides objective information based on actual measurements and observations. This helps to avoid subjectivity and human error and provides a more accurate assessment of the condition and utilization of land resources.
Fourth, remote sensing of land is a tool to improve transparency and openness in land management. Access to land cover data and information can be made available to the general public, stakeholders and scientific researchers. This facilitates the participation and involvement of various actors in the land management process.
However, it should be noted that remote sensing of land is only one tool for land management and should be used in conjunction with other methods and data sources. It is also important to take into account contextual and local characteristics, socio-economic factors and community needs when developing land management strategies. Remote sensing of land should be integrated into the broader context of land management, which includes consideration of legal, social, economic and environmental aspects.
An important aspect of land management using remote sensing is the development of skills and competencies in analyzing and interpreting data, and in making decisions based on the information obtained. Training of specialists and exchange of experience between different management bodies and research institutions play an important role in improving the efficiency and quality of land management.
Russian experience in land management using remote sensing of land is considerable. Russian satellites such as Kanopus and Resurs-P are actively used to collect information on the status of land use and monitor changes in land use. This allows for informed decisions on land planning and management at various levels.
In conclusion, land management using remote sensing of land is an effective and promising approach. It contributes to optimizing the use of land resources, controlling their use and protecting the environment. However, it is important to consider a wide range of factors and interests to ensure sustainable and equitable land management in accordance with the needs of society and nature.
Land resource management includes various methods and principles that help effectively utilize and preserve land resources. Below are some of them:
- Land Zoning. Zoning is a fundamental tool for land resource management. It involves dividing land parcels into different zones with specific designations (agricultural, industrial, residential, protected areas, etc.). Zoning enables the rational use of land resources, considering their potential and the needs of different economic and social sectors.
- Land Use Planning. Land use planning involves developing strategies, policies, and programs for land resource management. It is based on data analysis, land potential assessment, and consideration of socio-economic factors and community needs. The goal of land use planning is to optimize land resource utilization, maintain ecological sustainability, and ensure socio-economic development.
- Regulation and Licensing. Government and municipal authorities establish laws, rules, and norms regulating land use. This includes obtaining permits and licenses for land use, monitoring compliance with regulations, and applying sanctions in case of violations. Regulation and licensing help ensure the sustainable and responsible use of land resources.
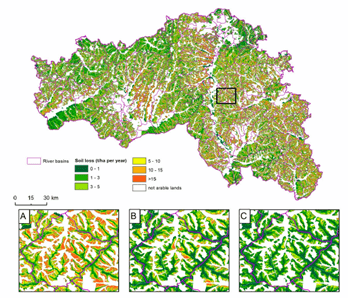
- Monitoring and Evaluation. Monitoring and evaluating land resource conditions are crucial management components. They provide up-to-date information on land use changes, soil conditions, water quality, and other environmental parameters. Monitoring and evaluation help identify problems, assess strategy effectiveness, and make informed decisions based on factual data. Remote sensing, geographic information systems, and other technologies play a vital role in land resource monitoring and evaluation.
- Public Participation. Public participation is an essential principle in land resource management. It involves engaging stakeholders, such as local residents, non-governmental organizations, and representatives from various economic sectors, in land use decision-making. Public participation promotes transparency, fairness, and legitimacy in land resource management.
- Ecological Sustainability. The principle of ecological sustainability entails preserving and restoring the ecological integrity of land ecosystems. Land resource management should consider the impact of human activities on nature, take measures to prevent soil degradation, water pollution, and biodiversity loss. Ecologically sustainable land management contributes to the long-term preservation of natural land functions and the maintenance of ecosystem services.
- Efficient Land Use. The principle of efficient land use involves maximizing the potential of land to meet social, economic, and environmental needs. It includes optimizing agricultural production, promoting sustainable urban planning, reducing land losses due to erosion and other processes, and rationally utilizing unused land parcels.
- Consideration of Rights and Interests. Land resource management should respect the rights and interests of various population groups, including local communities, indigenous peoples, and small-scale farmers. This includes protecting land rights, ensuring fair land resource distribution, and recognizing traditional land use systems. Considering rights and interests helps ensure fair and sustainable land management, prevent conflicts, and promote social justice.
- Integrated Approach. Land resource management should be carried out using an integrated approach that considers the interconnection of various land use aspects and balances economic, social, and environmental needs. An integrated approach fosters synergy between different policies and activities, ensures sustainable development, and minimizes negative environmental impacts.
- Continuous Learning and Research. Land resource management requires ongoing training and skill development for specialists, as well as scientific research to develop innovative methods and approaches. Education and research contribute to improving land resource management quality, enhancing practices, and enabling evidence-based decision-making.
These methods and principles of land resource management are interconnected and complement each other, ensuring the sustainable and efficient use of land. Their implementation requires collaboration among various stakeholders, effective use of information and technological resources, and consideration of contextual and local specifics in strategy and policy development.