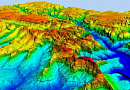
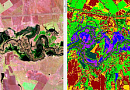
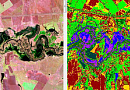
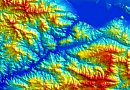
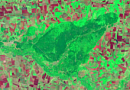
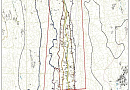
Aerial & UAV imagery is a method of capturing imagrs of the Earth's surface from a certain height using an aerial camera (e.g., unmanned aerial vehicle) mounted on an aircraft, with the aim of obtaining, studying, and presenting objective spatial data of the captured areas.
Aerial surveying is the process of obtaining images (aerial images) of the Earth's surface from a specific altitude. The survey is conducted using a camera installed on a manned or unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV).
Topographic aerial surveying is the process of obtaining aerial images of the Earth's surface and using them to create topographic maps. These maps depict the physical features of the terrain, including elevation, the location of natural and man-made objects, and the distribution of vegetation. Topographic aerial surveying is typically conducted using specialized cameras mounted on aircraft or unmanned aerial vehicles. The captured images are then processed to create accurate and detailed topographic maps, which can be used for various purposes, including urban planning, infrastructure development, and natural resource management.

You can order from us
Prices for services
|
Consultation |
Free |
|
Preliminary Analysis |
Free |
|
Aerial Images Execution |
The cost of Aerial & UAV imagery is calculated individually for each order and may vary: Minimum price for new imagery: 16,000 RUB per 1 km2 (up to 25 km2), and 8,000 RUB per 1 km2 (from 25 km2 to 100 km2). Prices for areas over 100 km2 are determined individually. Archival imagery: Starting from $5 per 1 km2. |
|
Execution Time |
The execution time for aerial photography is approximately 30 days from the prepayment. The duration depends on the time required for coordination with competent authorities, the time required for a representative of the military district headquarters to review the information that constitutes state secrets, and may be extended for significant volumes of work and remote locations. |
The cost of aerial photography depends on the area and location of the site, the quality requirements, and the type of photography (final product) - orthophotoplan, dense point cloud, CMM, CMR, 3D model, etc.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
Aerial & UAV imagery execution takes approximately 30 working days and is calculated individually for each project.
Delivery of archival aerial images takes around 10 working days (depending on the area).
The execution of aerial imagery depends on the total area of the territory, its remoteness, the time required to obtain flight permits, and the time for a control review. It also depends on the requirements for the imagery parameters and the final product. The timelines and costs are determined individually for each project.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
Results of Aerial & UAV imagerys
GEO INNOTER provides the buyer with the results of aerial imagery in the form of tiles or individual files in any convenient format. In addition to the classic options such as JPEG, PNG, and TIFF, we can also provide data in GeoTIFF format (which includes various types of geotags) and Google Earth KML/KMZ format (allowing the data to be opened in Google Maps, Google Earth, and ArcMap). Depending on the requirements of the technical specifications, orthophotoplans, point clouds, DSM, and DEM can be provided.
Requirements for Source Data
Accurate coordinates of the area of interest, specific requirements for aerial imagery (ground resolution, type of imagery, longitudinal and latitudinal overlap, minimum sun angle, time period for imagery), requirements for point cloud density (if needed), output data formats.
Additional Services
- Selection and ordering of aerospace materials
- Orthorectification and creation of digital orthophotoplans
- Forensic expertise
- Creation of cartographic materials
- Aerospace monitoring
- Creation of digital maps and topographic plans
Related services









Customers
FAQ
The provision of Aerial & UAV imagery services depends on a number of factors, with weather being the most important one. In spring, with the snow melting, the "hot" season begins, as it marks the peak of construction activities, advertising campaigns, large-scale earthworks, and extensive land surveys of various areas including forests and agricultural lands.
Over the past 5 years, aerial imagery has become closely integrated into the urban planning and updating of situational plans for urban and rural areas, where remote monitoring is required to identify illegal or non-compliant construction, update cadastral maps, and establish actual land use boundaries, thereby detecting unauthorized use.
Materials obtained through Aerial & UAV imagery are used in a wide range of fields, including:
- Geodesy for creating situational and topographic plans;
- Surveying to obtain accurate information on mining samples, the location of valuable minerals, and the placement of large underground objects;
- Cadastre services for obtaining detailed plot plans;
- Nature conservation to monitor the development and movement of populations, the quality of green vegetation growth, fire control, and the ecological status of natural objects;
- Agriculture for monitoring crop development and root vegetable storage;
- Construction, where aerial images with unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) allows for effective land planning and visualizing how constructed objects fit into the surrounding landscape;
- Military purposes for capturing images of training grounds, identifying suitable locations, and more.
Licenses
Warranty
We guarantee 100% quality of services. Cooperating with GEO Innoter specialists, you exclude risks and losses!The availability of qualified personnel with extensive experience in working with specialized software allows us to ensure timely and quality work! Our team works not only throughout Russia, but also in CIS countries.