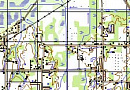
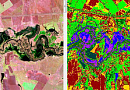
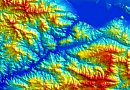
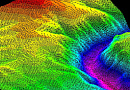
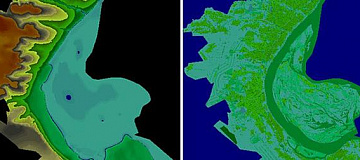
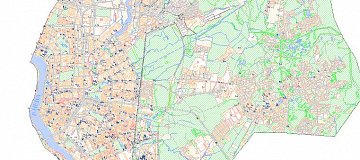
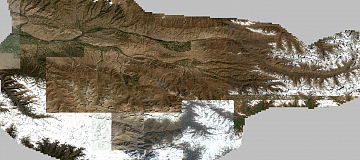
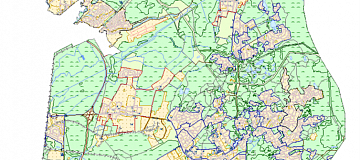
Radio frequency mapping (RF mapping), is the process used to create a visual representation of wireless signal coverage within a given area. Such maps help identify locations where the signal is strong or weak, enabling optimization of the wireless network.
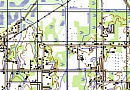
Digital maps for telecom (RF Map) are used for detailed network planning in remote areas with dense development, where urban stations are constantly being relocated while ensuring compliance with radio wave propagation requirements.
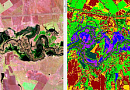
Regional 2D telecom models (digital terrain maps) are applied for coverage, supporting efficient development and modernization of communication networks that cover large territories.
The components of digital terrain models for Telecom include:
-
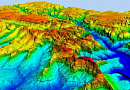
High-precision 3D / 2.5D / 2D models
-
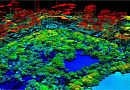
Clutter 3D / 2.5D / 2D models for accurate radio planning
-
Digital 3D / 2.5D / 2D terrain models
-
Digital 3D / 2.5D height elevation models
-
Orthomosaics for context mapping
-
Comprehensive address and infrastructure databases

You can order from us
Prices for services
| Consultation | Free |
|---|---|
| Preliminary analysis of the availability of source data, additional and reference materials | Free |
| Order of satellite imagery | from $0.5 to $70 USD per 1 km2 depending on the type of imagery (archive/new, mono/stereo, resolution)* |
| Cost of creating CMM (Digital Terrain Maps) | from $1 USD per 1 km2, calculated individually for each specific order and depends on the amount of processed remote sensing data, the presence/absence of ground control points, and the used CMR (Digital Elevation Model). |
| Cost of creating (updating) 3D/2.5D/2D digital terrain models | The cost of creation depends on the complexity category, execution time, and the number of square kilometers. The cost of updating depends on the degree of obsolescence of the previously created project but does not exceed 50% of the creation cost. |
| Execution time | From 20 working days (depends on the volume, complexity category, availability of remote sensing materials, additional, and reference materials) |
The price of creating CMM depends on the cost of ordered satellite imagery and the complexity of the work (the number of images covering the area of interest, the presence of ground control points, and the complexity category of the area). It is calculated individually for each client.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
Coordination of issues, analysis of the availability of remote sensing data, source map materials, additional and reference data: from 1 to 5 days*Conclusion of the contract: from 1 to 5 days*
Taking pictures: from 3 to 10 days **
Request, receipt of the original map material in the CGKiPD (if necessary): from 1 to 20 days*
Creation of a PSC: from 5 days*
Decryption and vectorization: from 15 days*
Summary of adjacent sheets, execution of controls: from 5 to 10 days*
Preparation of the report: from 5 to 10 days
TOTAL TERM: from 20 days*
* working days
** from the date of receipt of 100% advance payment for remote sensing materials
The timing of the work depends on the number of square kilometers, the scale and type of products being created, the availability of archival remote sensing materials, additional and reference materials.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
The customer receives 3D/2.5D/2D digital terrain models (Digital Elevation Model, Height Model of Obstacles, Clutter Model, Vector Model, Address Database), orthophotoplans, additional reference materials, and a technical report.
The digital models are fully compatible with the planning tool Mentum Planet, and they can also be provided in formats compatible with programs such as ASSET, ATOLL, Mapinfo, etc. (as per the customer's requirements).
All results are delivered on electronic media or via the Internet through FTP servers, and the textual materials are also duplicated in printed form.
Requirements for Source Data
To perform high-quality preliminary work, the following information must be provided:
- Coordinates of the mapping area (in any convenient form)
- Type of telecom models to be created (updated), format of representation, in which gradation to provide data, projection, coordinate system, and heights
- Availability of source cartographic materials, additional, and reference data
- Availability of coordinate lists of reference points for photogrammetric processing of remote sensing materials
- Requirements for the object composition, thematic information of the created (updated) data project
- The need for the development and approval of Editorial and Technical Instructions for the creation (updating) of data projects
Technical Characteristics of 3D, 2.5D, 2D Telecom Models
| Model Type | Urban Model | Urban Model | Regional Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3D | 2.5D | 2D | |
| Plan Accuracy (RMSE, m) | |||
| Buildings and other distinct contours | 3 | 5 | 50 |
| Contours of vegetation and soils | 5 | 7 | 70 |
| Values for mountainous and desert areas | N/A | N/A | 100 |
| Height Accuracy (RMSE, m) | |||
| On plains | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| On rugged, hilly, and sandy territories | 1.5 | 2.5 | 7 |
| In low-mountain and medium-mountain areas | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| In high-mountain territories | N/A | N/A | 20 |
If there is no possibility to provide the specified information, it is necessary to provide information about the purpose of the project, what types of work are planned to be performed using the project, and the specialists of "GEO "INNOTER" will analyze the information and prepare an optimal offer for creating (updating) the data project.

Related services




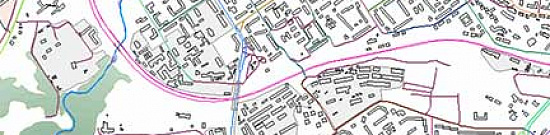





Completed projects

Customers
FAQ
- the territory of interest (location / coordinates of the object in any convenient form, and the area of the object);
- a specific task that needs to be solved with the use of CMM
- As the main material for creating (updating) the data project, remote sensing materials available in the archives of spacecraft operators for the most current date are used, or a new survey is ordered. High accuracy of all parameters is ensured through the use of stereo pairs of high-resolution satellite images and ultra-high-resolution UAV data or aerial imagery.
- When creating (updating) a data project, additional and reference materials are used in the form of various geographical descriptions, maps and atlases of a larger (small) scale, reference books, as well as data available to the Customer.
- Cartographic products available in public and private funds or cartographic products provided by the Customer can be used as updated telecom models.
Data is provided in formats specified by the Customer according to the requirements of the technical assignment and compatible with ASSET, ATOLL, Mapinfo, and other software (as per the customer's requirements).
The recommended software for using CMM is the ONEPLAN solution.
| Clutter Model Parameters |
| Resolution (cell size) - 1 m |
| Planimetric Accuracy (x, y) - 1-3 m |
| Class Name / Class Description |
| 1 Open_Area / Open space |
| 2 Wood / Forest |
| 3 Park / Parks, gardens, and alleys |
| 4 Tree / Individual trees |
| 5 Habitation / Residential building |
| 6 Shack_House / Private sector building and territory |
| 7 Industry / Buildings and territory of industrial purpose |
| 8 Monument / Monuments, steles, monolithic objects |
| 9 Water_Bridge / Bridge over the river |
| 10 Road Bridge / Bridge over the road |
| 11 Water / Water surface |
| 12 Road / Roads |
| 13 Railway / Railways |
| 14 Rural Buld-Up Area / Quarters of low-rise buildings up to 6m in height |
| 15 Urban Buld-Up Area / Urban quarters with dense buildings over 6m in height |
Licenses
Warranty
We guarantee 100% quality of services. By cooperating with GEO Innoter specialists, you eliminate risks and losses!The availability of qualified personnel with extensive experience in working with specialized software makes it possible to guarantee timely and high-quality performance of work!