
You can order from us
Prices for services
| Consultation | Free |
|---|---|
| Preliminary analysis | Free |
| Radar image order | Starting from $1000 per scene depending on the imaging (archive vs. new, resolution) * |
| Turnaround time | From 5 working days (depending on volume, complexity, availability of archive imagery) |
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
Technical task coordination: 1 to 5 days*Contract signing: 1 to 5 days
Image acquisition: 3 days**
Image processing: 1 to 3 days
TOTAL TIME: 5 days*
business days
** from the date of receiving 100% advance payment
The turnaround time depends on the total area of the survey, the number of processed images, and is calculated individually for each customer.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
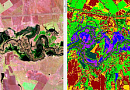
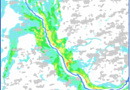
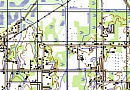
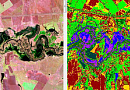
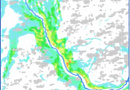
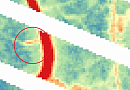
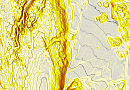
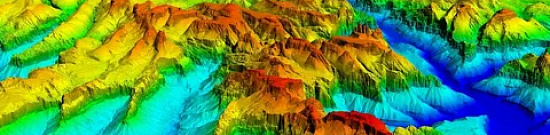
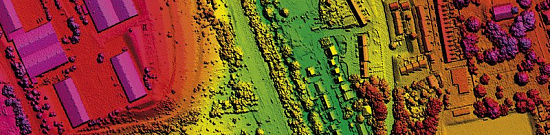
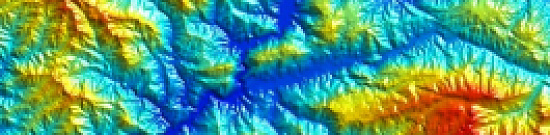
Creation of the final product based on space radar survey materials:
- Archival radar images
- Materials from new space radar surveys
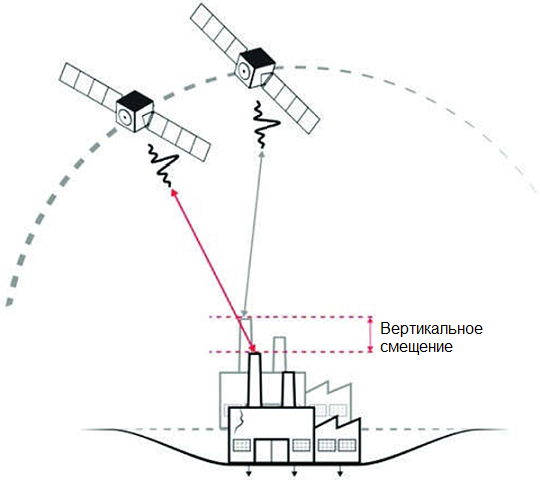
- Materials from space radar interferometric surveys
GEO INNOTER delivers the ready-made products to the customer who requested the space survey materials, according to the Technical Task, on electronic media or via the Internet through FTP servers.
Requirements for source data
Accurate coordinates of the area of interest, requirements for the space survey materials (resolution on the ground, type of survey, survey period).
If it is not possible to provide the specified information, please provide information on the intended use of the remote sensing materials, and GEO INNOTER specialists will analyze the requirements and offer an optimal solution to the problem.
Related services








Aerophotogeodesist, work experience 58 years, Education - Moscow Institute of Geodesy, Aerial Survey and Cartography (MIIGAiK)
Customers
FAQ
- Area of interest (location / coordinates of the object in any convenient format, and the area of the object)
- Date or time interval for which archival imagery can be searched or new imagery can be acquired
- Requirements for the survey (angle of the image, sun angle, resolution, type of survey, cloud cover)
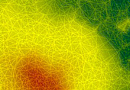
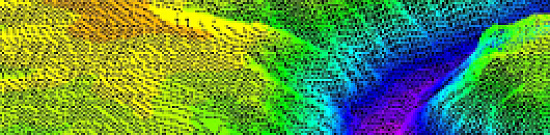
- Single Look Complex (SLC) image - information obtained through the focusing of the transmitted signal. The radar image at this processing level includes two channels: an amplitude ("panchromatic") image in grayscale and a phase image of the signal, which is used for creating digital elevation models and displacement maps of the Earth's surface.
- Geocoded image - The radar image is spatially referenced in a specific coordinate system. Radar images at this processing level are typically delivered in GeoTIFF format.
- Orthorectified image - High-quality radar image without geometric distortions caused by terrain. Radar satellite imagery at this processing level is used for cartographic materials and spatial analysis.
Licenses
Warranty
We guarantee 100% quality of service. By collaborating with the specialists of GEO Innoter, you eliminate risks and losses!
Having qualified staff with extensive experience in working with specialized software allows us to guarantee timely and high-quality execution of work!
Advantages of collaborating with GEO Innoter
- Many years of experience;
- Direct distribution agreements with satellite imagery operators;
- Experience in executing projects of any complexity, both with aerial photography and satellite imagery;
- Availability of modern software for processing remote sensing data;
- Significant server capacities for processing remote sensing data;
- A team of highly skilled professionals in the field of cartography and photogrammetry.