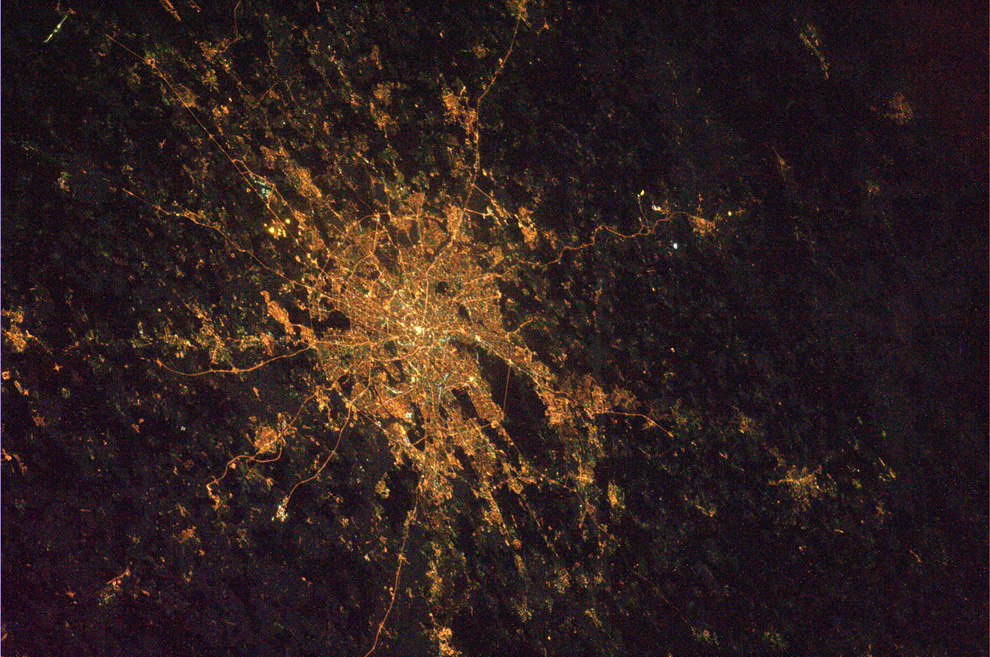
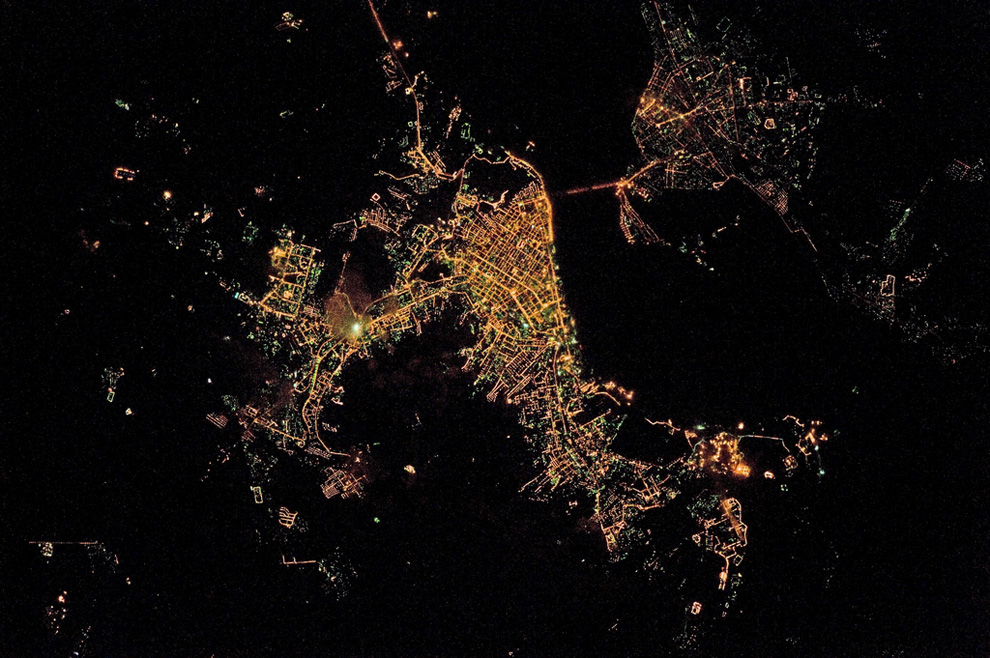
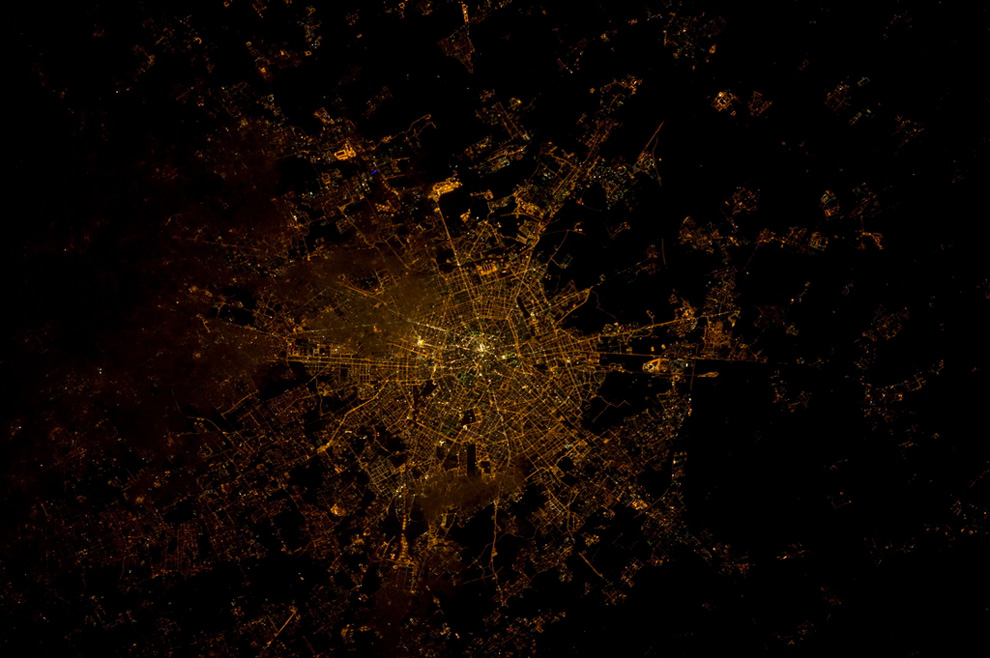
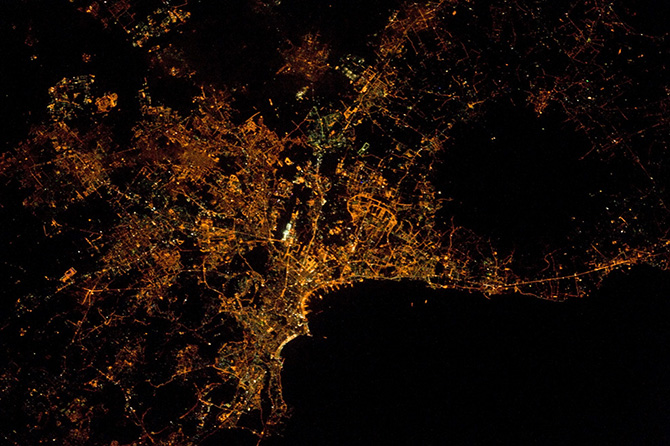
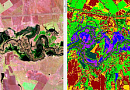
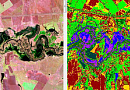
Uses of nighttime satellite imaging:
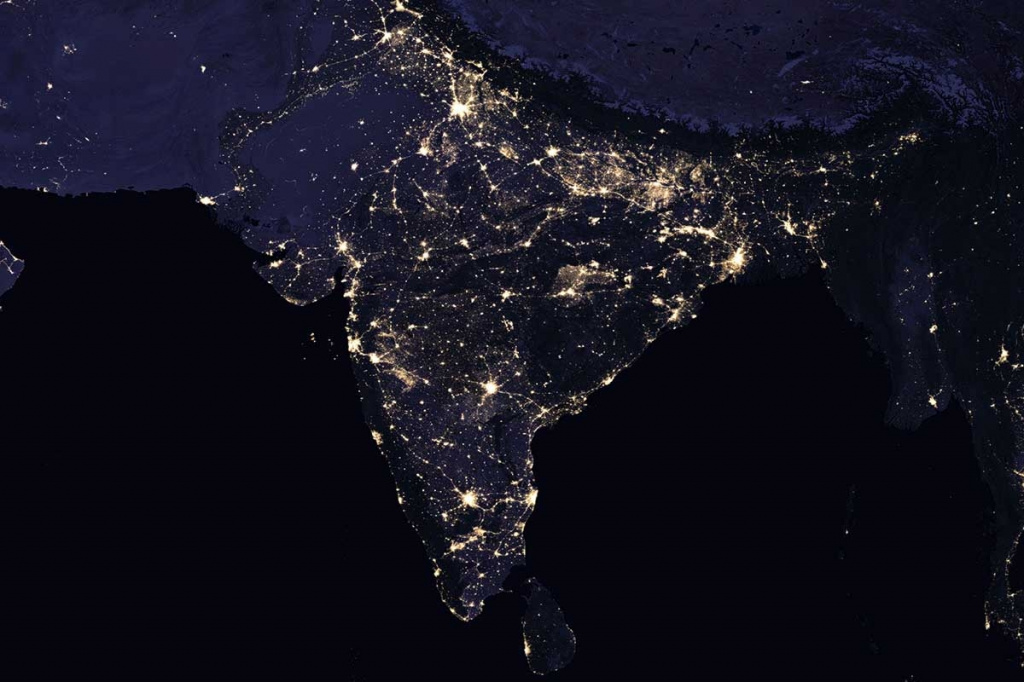
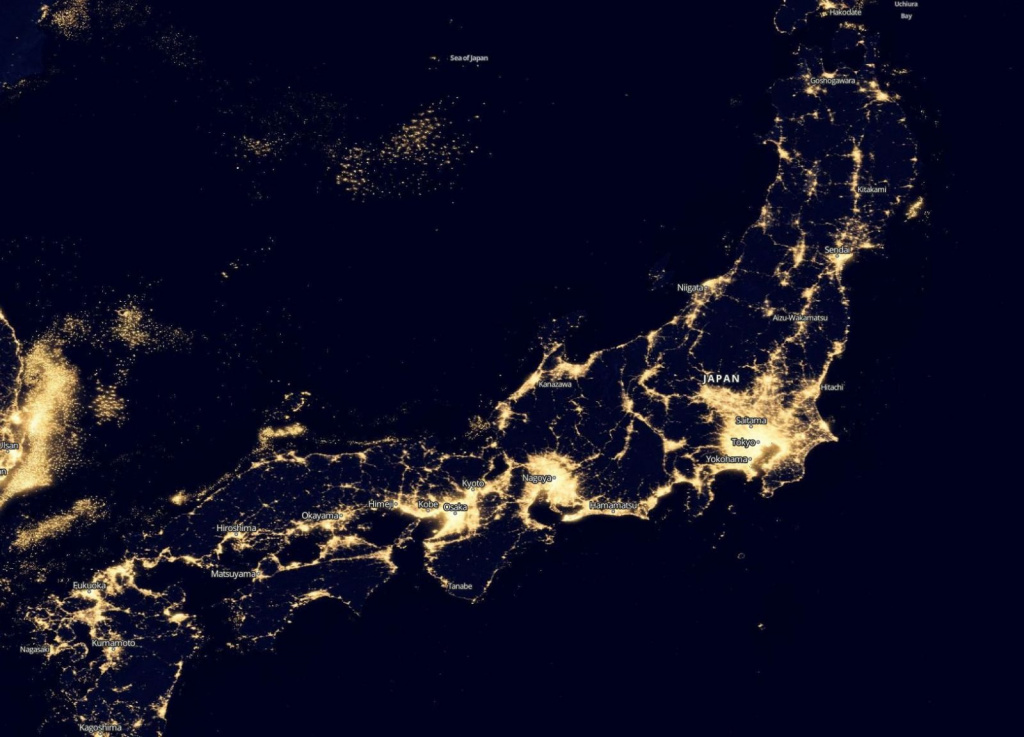
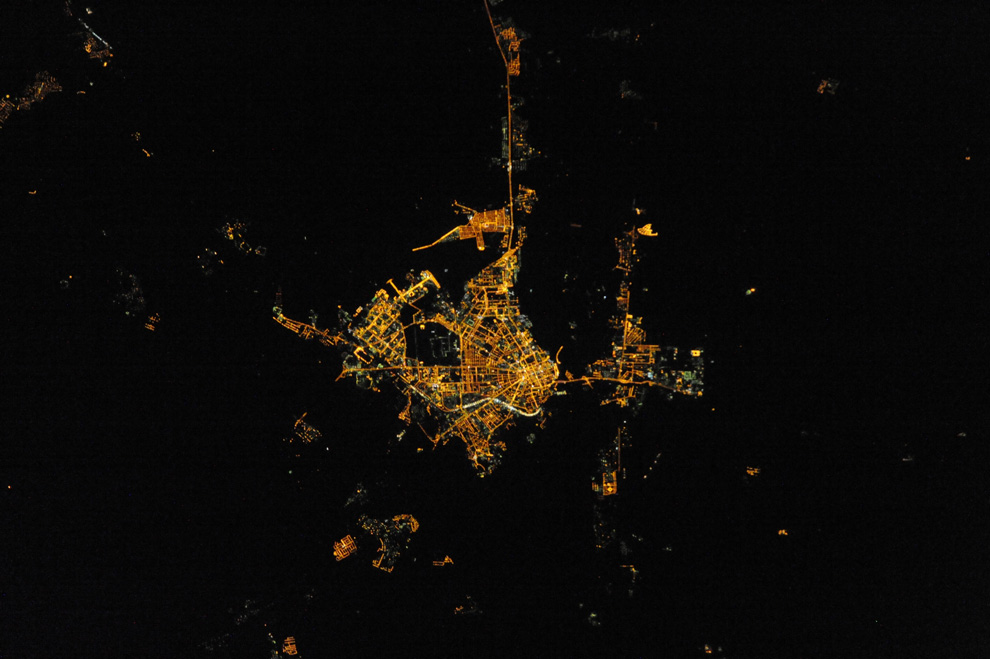
Nighttime satellite imagery is created by detecting emissions from human activity on the planet, including infrastructure (city lights, villages, towns, industrial and agricultural facilities, mining, gas flares, fishing vessels, etc.) and natural lights such as fires, lightning, moonlight, microorganisms, and animals.Satellite images of nighttime lighting have been used for decades as a global data source to study a wide range of socio-economic factors.

You can order from us
Prices for services
| Events | Free / cost per unit |
|---|---|
| Consultation | Free |
| Selection of images, preliminary analysis | Free |
| Ordering pictures |
From $5 to $40 per 1 km2 depending on the imaging type (archive or new) and resolution* |
| Period of execution | From 5 working days (depends on the volume, complexity category, and availability of archive images) |
* - if the Client does not provide their materials or it is not possible to use free images.
The price of nighttime satellite imaging is calculated individually for each Client.
The cost of execution is calculated on an individual basis, taking into account a specific of task.
After receiving the task description, we calculate the cost and send you a commercial offer.
Period of execution
The timeframe for nighttime satellite imagery depends on the following factors:
- Work execution period - from 5 (five) working days, calculated individually for each client.
- Work execution period depends on the total area of imaging, the number of processed images, and their type (mono-stereo), calculated individually for each client.
How to place an order:
Need for consultation?
Fill the form and we will contact you
Stages of service provision
The result of the provision of services
Creation of the final product based on nighttime satellite imaging materials:
- Nighttime satellite images of various types: black and white, color, multi-zone, synthesized;
- Thematic nighttime satellite imaging materials of various types, according to the specified directions above;
- Nighttime radar satellite imaging materials (by agreement with the Client) for comparative analysis with IR nighttime imaging;
- Maps, topographic and thematic, according to the tasks set by the Client;
- Analytical and statistical reports describing the obtained nighttime imaging data and providing useful recommendations for decision-making for the Client.
GEO INNOTER provides the Client who requested satellite imaging materials with the finished product according to the Technical Specifications on electronic media or through the Internet via FTP servers.
Requirements for Source Data
Accurate coordinates of the area of interest, requirements for satellite imaging materials (resolution on the ground, type of imaging, maximum angle of the image, maximum allowable percentage of cloud cover, nighttime period for imaging).
If it is not possible to provide the specified information, provide information about the purpose of using remote sensing materials, and the specialists of GEO INNOTER will analyze the requirements and suggest an optimal solution to the problem
Related services



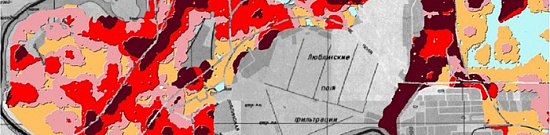






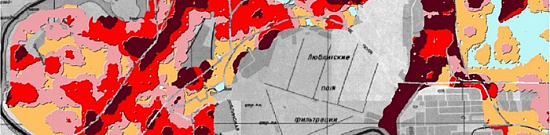
Completed projects

Customers
FAQ
As of 2024, the best group of satellites for tasking night images is Jilin 1 Video 04/05/06/07/08
The satellites uses 0.55 to 0.75 micrometer (um) channel to detect this reflected sunlight, it cannot be used during night.
As of 2024, the best group of satellites for tasking night images is Jilin 1 Video 04/05/06/07/08
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): SAR is an active sensor that emits microwave pulses and measures their reflections. It can operate day and night, regardless of natural light conditions. SAR is particularly useful for capturing images in low light or complete darkness.
- Infrared Imaging: Some satellites are equipped with infrared sensors that can detect heat emitted by objects on the Earth's surface. These sensors can capture images during the night since they do not rely on visible light.
- Day/Night Band (DNB): Some Earth observation satellites have a day/night band that can capture low-light imagery using available moonlight and ambient light sources such as city lights.
- City Lights: Urban areas are illuminated by streetlights, buildings, and other artificial lighting sources, creating distinct patterns and clusters of light. Major cities around the world stand out prominently.
- Coastlines: The outlines of coastlines and islands are often visible due to the lights from populated areas along the shores.
- Airports: Airports are recognizable by the arrangement of runway lights, apron lights, and the patterns created by the movement of aircraft.
- Road Networks: Highways and major roads are visible as linear patterns of light, connecting cities and regions.
- Oil and Gas Infrastructure: Lights from offshore oil rigs and gas platforms can be observed in certain regions.
- Auroras: In polar regions, particularly near the North and South Poles, the auroras (aurora borealis in the Northern Hemisphere and aurora australis in the Southern Hemisphere) can be seen as colorful displays of light caused by interactions between charged particles and the Earth's atmosphere.
Wildfires: Intense wildfires can produce significant light sources that are visible from space.